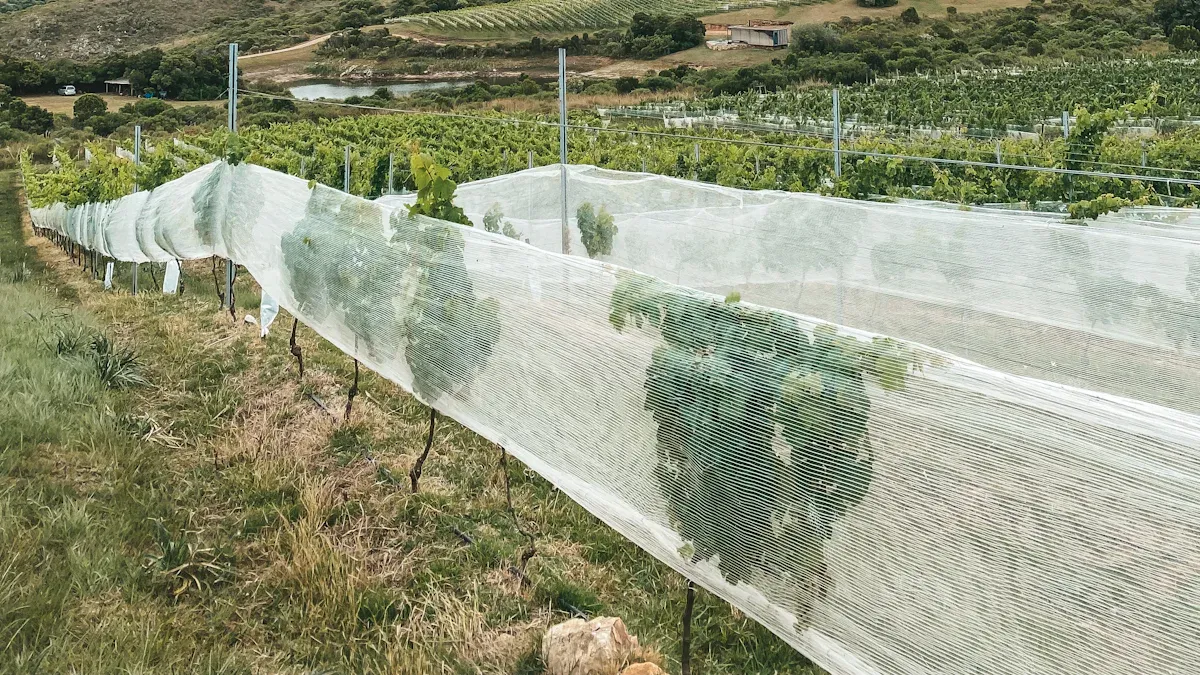
Choosing the right agriculture nets plays a key role in helping farmers protect crops and improve yields. Every crop faces unique challenges from pests, birds, or harsh weather.
Matching the shade percentage, mesh size, and material to the crop’s requirements allows growers to create optimal growing conditions.
Define Your Crop Protection Needs
Crop-Specific Requirements
Every crop has unique needs. Some crops need more sunlight, while others require protection from intense heat. For example, leafy greens often thrive under partial shade, but fruiting plants like tomatoes may need more direct sunlight.
Farmers should identify the specific requirements of their crops before choosing netting.
Common Threats: Pests, Birds, Weather
Crops face many threats in the field. Insects can damage leaves and fruit. Birds may eat seeds or ripe produce. Weather events like hail, strong winds, or heavy rain can destroy plants in minutes. Farmers must identify the main threats to their crops.
This step helps them select the right agriculture nets for protection.
- Pests: Insects such as aphids, whiteflies, and beetles can reduce yield and quality.
- Birds: Birds often target seeds, berries, and young plants.
- Weather: Hail, wind, and excessive sun can cause physical damage or stress to crops.
Climate and Environmental Factors
Local climate plays a big role in net selection. Areas with high sun exposure may require nets with higher shade percentages.
Regions with frequent storms or strong winds need stronger, more durable netting. Farmers should also consider humidity and temperature.
Select Agriculture Nets Types According to Your Needs
Choosing the right types of netting helps farmers protect crops and improve yields. Each type serves a unique purpose and fits different applications. Understanding these options allows growers to select the best agriculture nets for their needs.
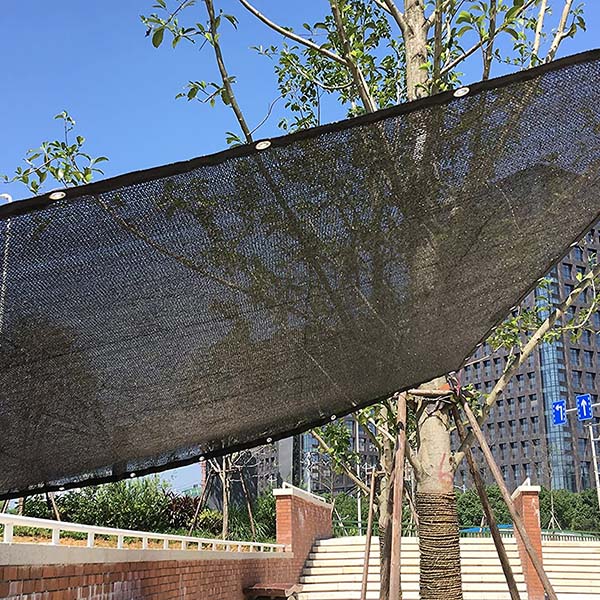
Shade Nets
Shade nets and shade cloth provide essential protection from intense sunlight. Farmers use shade cloth to control the amount of shade their crops receive.
Shade cloth comes in many densities, offering different levels of shade. Some crops need 30% shade, while others thrive under 50% or even 75% shade.
Shade cloth helps prevent sunburn and reduces heat stress. Shade cloth also helps maintain soil moisture by reducing evaporation. Many growers use shade cloth in greenhouses, nurseries, and open fields. Shade cloth can also protect young plants from wind and light rain.
Anti-Bird Nets
Anti-bird nets keep birds away from valuable crops. These types of netting use strong, lightweight material with small openings. Anti-bird nets work well for fruit trees, vineyards, and berry bushes.
Farmers stretch anti-bird nets over plants or build frames to support them. Anti-bird nets prevent birds from eating seeds, fruit, and young plants. These nets help reduce crop loss and improve harvest quality.
Insect Nets
Insect nets protect crops from harmful insects. These types of netting have fine mesh that blocks pests like aphids, whiteflies, and beetles. Insect nets allow air and light to pass through while keeping insects out. Farmers use insect nets in greenhouses, tunnels, and open fields. Insect nets help reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
Hail Protection Nets
Hail protection nets shield crops from hail damage. These types of netting use tough, flexible material that absorbs the impact of hailstones. Hail protection nets cover orchards, vineyards, and vegetable fields.
They help prevent bruising and breakage, saving crops from severe weather.
Key Features of Agriculture Protection Netting
Material Quality (HDPE)
Material quality stands as the foundation of effective agriculture protection netting. Most high-quality nets use high-density polyethylene (HDPE) because this material resists stretching, tearing, and chemical damage. HDPE also provides flexibility, which helps during installation and removal.
Farmers rely on HDPE for its lightweight nature and its ability to withstand repeated use in different environments. Agriculture protection netting made from HDPE supports a wide range of shade cloth applications, from greenhouses to open fields. HDPE does not absorb water, so it dries quickly after rain. This feature helps prevent mold and mildew growth.
Farmers should always check the thickness and weave of the HDPE to ensure the netting meets their specific needs. Strong HDPE nets last longer and provide better protection for crops.
UV Resistance
Sunlight can weaken many materials over time, but UV-resistant agriculture protection netting stands up to harsh rays. UV resistance ensures that nets do not become brittle or fade after long exposure to the sun.
This feature is especially important for shade cloth, which often covers crops for months at a time. UV-resistant shade cloth maintains its color and strength, even in regions with intense sunlight. Farmers who use UV-stabilized agriculture protection netting see fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs.
UV resistance also helps nets keep their shape and flexibility, which is vital for repeated shade cloth applications. When selecting agriculture protection netting, always look for products labeled as UV-stabilized or UV-treated.
Mesh Size and Strength
Mesh size determines what passes through the agriculture protection netting. Fine mesh blocks small insects, while larger mesh sizes keep out birds or hail. The right mesh size depends on the crop and the main threats in the area.
For example, insect nets use very fine mesh to stop aphids and whiteflies, while anti-bird nets use larger openings. Mesh strength also matters. Strong mesh resists tearing from wind, animals, or falling branches. Shade cloth with reinforced edges and sturdy mesh stands up to tough conditions. Farmers should match mesh size and strength to their crop’s needs and the local environment.
Color and Shade Percentage
Color and shade percentage play a major role in how agriculture protection netting affects crops. Shade cloth comes in many colors, including green, black, white, and sometimes blue.
Each color changes the amount and quality of light that reaches the plants. For example, black shade cloth absorbs more heat, while white shade cloth reflects sunlight and keeps crops cooler. Green shade cloth offers a balance between light absorption and reflection.
Shade percentage tells how much sunlight the net blocks. Farmers can choose shade cloth with 30%, 50%, 70%, or even 90% shade, depending on the crop’s needs. High shade percentages protect delicate plants from sunburn, while lower percentages suit sun-loving crops. Agriculture protection netting with the right color and shade percentage supports healthy growth and better yields.
Sizing and Installation Tips

Basic Installation Guidelines
Proper installation protects crops and extends the life of agriculture nets. Farmers should start by clearing the area of sharp objects that could damage the net.
They should lay out the net and check for any defects before installation. Using sturdy poles, wires, or frames helps support the net and keeps it in place. Farmers should stretch the net evenly and secure it with clips, ties, or stakes.
Tight installation prevents sagging and reduces wind damage. Regular inspection after installation helps catch any issues early. Different installation methods work for different crops and structures, so farmers should choose the best approach for their needs.
Cost and Value Considerations
Price Range and Budget
Agriculture nets come in a wide range of prices. The cost depends on the type, size, and features of the net. Farmers should set a clear budget before making a purchase. They can compare different products by looking at material quality, mesh size, and the level of protection.
Some nets may seem expensive at first, but they often include extra features like UV resistance or reinforced edges. Farmers should also consider the cost of installation. Some nets require special tools or extra labor for installation, which can add to the total price. Planning for these expenses helps avoid surprises.
Lifespan and ROI
The lifespan of agriculture nets affects their value over time. High-quality nets made from strong materials can last several years with proper installation and care.
Farmers should check the expected lifespan before buying. Longer-lasting nets may cost more, but they often provide better value. Return on investment (ROI) improves when nets protect crops for many seasons. Good installation also helps extend the life of the net.
Regular inspection and quick repairs prevent small problems from becoming costly. Farmers who invest in durable nets and proper installation often see higher yields and lower replacement costs.
Balancing Quality and Cost
Farmers must balance quality and cost when choosing agriculture nets. Cheaper nets may save money at first, but they often wear out faster or need more repairs.
High-quality nets with strong materials and good installation offer better protection and last longer. Farmers should look for nets that match their needs and fit their budget.
They can also save money by learning proper installation techniques. Some suppliers offer guides or videos to help with installation. Investing in quality nets and careful installation leads to better crop protection and long-term savings.
Maintenance and Care for Agriculture Nets
Cleaning and Storage
Proper cleaning keeps agriculture nets effective and extends their lifespan. Farmers should remove debris, leaves, and dirt from the nets after each season. They can use a soft brush or low-pressure water spray to clean the surface.
Avoid using harsh chemicals, as these can weaken the net material. After cleaning, allow the nets to dry completely before storing them. Store nets in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Fold or roll the nets neatly to prevent creases and tangles. Good storage practices help prevent mold, mildew, and damage during the off-season.
Repair Tips
Small tears or holes can appear in agriculture nets over time. Quick repairs stop these problems from getting worse. Farmers can use repair kits or strong thread to stitch up minor rips. For larger holes, patching with a piece of similar netting works well. Secure the patch with weather-resistant adhesive or by sewing.
Regular checks help spot damage before it spreads. Keeping a basic repair kit on hand saves time during busy seasons.
Conclusion
Choosing agriculture nets requires careful attention to crop needs, material, shade, and mesh size. Shade cloth offers many options for shade and protection. Farmers should compare shade cloth types, shade percentages, and shade cloth colors.
Shade cloth with the right shade percentage matches every crop. Shade cloth with ongoing care protects every harvest. Shade cloth with the right features brings the best results.













